Nursing Management of Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
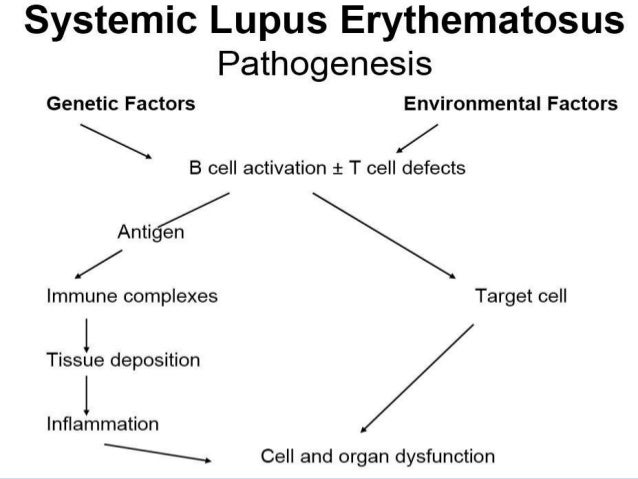
Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE) is a chronic, multisystem, inflammatory, autoimmune disorder characterised by formation of autoantibodies directed against self-antigens and immune-complex formation resulting in damage to essentially any organ.
Clinical Manifestations :
Assessment and Diagnostic Findings :
Diagnosis of lupus is difficult because sign and symptoms vary considerably from person to person. Signs and symptoms lupus may vary over time and overlap with those of many other disorders. No one test can diagnose lupus. The combination of blood and urine tests, sign and symptoms and physical examination findings leads to the diagnosis .
Laboratory and imaging tests include :
1. Complete Blood count
2. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
3. Kidney and liver assessment
4. Antinuclear antibody ( ANA ) test
5. Chest X-ray
6. Echocardiogram
7. Urinalysis
The American College of Rheumatology has established criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematous involving these 11distinct elements:
The diagnosis of SLE is generally made if 4 of the 11 criteria are present, either serially or simultaneously .
Nursing Care plan of Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematous :
As a nurse , our first priority should always be the proper assessment of patient's condition and look thoroughly for subjective data and objective data before planning the nursing care . Some of the common diagnosis and interventions for them respectively are listed below.
1. Impaired skin integrity related to exacerbation of disease process / inflammation / vasoconstriction possibly evidenced by red rashes/ skin breakdown/ itching/ scalp hair loss
Interventions :
a) Assess the skin for integrity as small lesions may occur on oral or nasal mucous and maculo-papular rashes may be seen on patient's face or chest region.
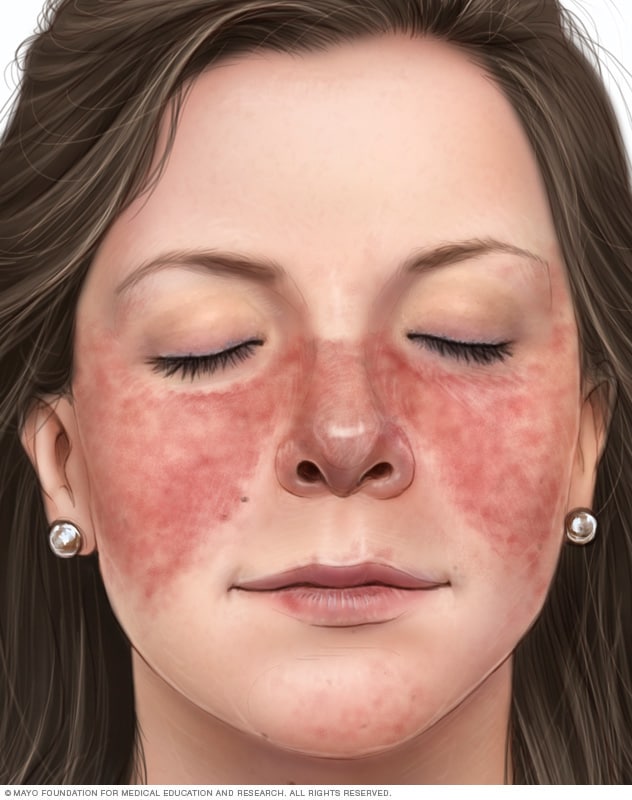
b) Assess the classic butterfly rash which may be present across the bridge of the nose and on the cheeks .
c) Assess for photosensitivity in patient to confirm the severe response of rashes in exposure to UV or sunlight.
d) Encourage adequate nutrition and hydration for promoting healthy skin and wound healing.
e) Instruct the patient to clean and moisturize the skin in order to reduce dryness and maintain skin integrity.
f) Introduce recommended prophylactic pressure relieving devices like elbow pads and special mattress to aid in prevention of skin breakdown.
g) Encourage patient to wear SPF 15 or above cream , protective eye glasses and carry umbrella in order to protect skin from sunlight exposure.
h) Instruct patient to avoid spicy foods as these foods might irritate ulcers in oral membranes.
i) Explain the patient that the scalp hair loss may not be permanent and will regrow as the disease subsides and dose of corticosterioids and immunosuppresant drugs are tapered down.
j) Encouarge patient to conceal the hair loss in their own ways ( e.g. wearing scarves, hats, wigs ) to ease the lifestyle .
Interventions :
a) Assess the patient's description of pain. Patient's usually experience arthralgias of many joints, joint stiffness and discomfort.
b) Assess the signs of joint inflammation like warmth, redness, swelling or the signs of decreased movement.
c) Assess and study the measures used for patient to alleviate pain previously in order to plan and manage the pain with new measures .
d) Encourage the use of ambulation aids like crutches, walkers so as to absorb some weight from inflamed extremity.
e) Place the patient in anatomically correct position with all joints to prevent the development of contractures.
f) Demonstrate and encourage to perform Range of motion exercise to maintain joint mobility.
g) Encourage the patient to take 15 minutes warm shower if possible to relieve stiffness and pain.
h) Use divertional therapy or relaxation therapy to diminish pain.
i) Administer prescribed anti-inflammatory medications early in the morning with small snack or breakfast.
j)Counsult with physiotherapist for the proper splinting of joints .
k) encourage patients to wear splints as ordered to reduce muscle spasm.
Interventions :
a) Assess the client's description of fatigue, usual time of feeling it, aggravating and alleviating factors.
b) Determine if the fatigues is related with any psychological factors like stress or depression because its the common problem in patients with chronic disease .
c) Reinforce energy conservation activities like taking rests periods and maintaing pace.
d) Organize all the activities and environment beforehand to conserve energy and reduce fatigue.
e) Instruct patient to avoid caffeine and other stimulating food before bed as it can contribute to fatigue and interrupt sleep pattern.
f)Encourage a warm bath or washers immediately before bedtime for relaxation.
f) Reposition the patient in certain time periods to promote comfort .
g) Administer a night time analgesic and / or a long acting anti-inflammatory drug as prescribed to alleviate pain and facilitate sleep.
Interventions:
a) Assess the patient's knowledge of disease , management and complication .
b) Educate the disease process information as the unknown case, chronicity of SLE, processes of inflammation, control versus cure.
c)Introduce information on drug therapy and instruct patient about potential side effects of steroids, immunosuppresant drugs.
d) Patient should be stressed on not altering or stopping steroids as they wish .
e) Instruct the patient to monitor for signs of fever as it is a common manifestation of SLE.
f) Instruct in adapting a healthy lifestyle activities that helps to reduce flare-ups such as eating a balanced diet, regular exercise, avoiding sun, adequate rest.
g) Provide information on appropriate clinical trials .
h) Always be cooperative and a good listener to patient's misunderstanding or concerns about disease.
Prepared by : RN Dawa Lhomu Sherpa (Yangla )
BSc. Nurse , Nepal
b) Assess the classic butterfly rash which may be present across the bridge of the nose and on the cheeks .
c) Assess for photosensitivity in patient to confirm the severe response of rashes in exposure to UV or sunlight.
d) Encourage adequate nutrition and hydration for promoting healthy skin and wound healing.
e) Instruct the patient to clean and moisturize the skin in order to reduce dryness and maintain skin integrity.
f) Introduce recommended prophylactic pressure relieving devices like elbow pads and special mattress to aid in prevention of skin breakdown.
g) Encourage patient to wear SPF 15 or above cream , protective eye glasses and carry umbrella in order to protect skin from sunlight exposure.
h) Instruct patient to avoid spicy foods as these foods might irritate ulcers in oral membranes.
i) Explain the patient that the scalp hair loss may not be permanent and will regrow as the disease subsides and dose of corticosterioids and immunosuppresant drugs are tapered down.
j) Encouarge patient to conceal the hair loss in their own ways ( e.g. wearing scarves, hats, wigs ) to ease the lifestyle .
2. Acute pain related to inflammation associated with increased disease activity possibly evidenced by facial grimace / verbalized complaint .
Interventions :
a) Assess the patient's description of pain. Patient's usually experience arthralgias of many joints, joint stiffness and discomfort.
b) Assess the signs of joint inflammation like warmth, redness, swelling or the signs of decreased movement.
c) Assess and study the measures used for patient to alleviate pain previously in order to plan and manage the pain with new measures .
d) Encourage the use of ambulation aids like crutches, walkers so as to absorb some weight from inflamed extremity.
e) Place the patient in anatomically correct position with all joints to prevent the development of contractures.
f) Demonstrate and encourage to perform Range of motion exercise to maintain joint mobility.
g) Encourage the patient to take 15 minutes warm shower if possible to relieve stiffness and pain.
h) Use divertional therapy or relaxation therapy to diminish pain.
i) Administer prescribed anti-inflammatory medications early in the morning with small snack or breakfast.
j)Counsult with physiotherapist for the proper splinting of joints .
k) encourage patients to wear splints as ordered to reduce muscle spasm.
3. Fatigue related to anaemia / depression / disease condition possibly evidenced by excessive sleeping / decreased performance / lack of energy.
Interventions :
a) Assess the client's description of fatigue, usual time of feeling it, aggravating and alleviating factors.
b) Determine if the fatigues is related with any psychological factors like stress or depression because its the common problem in patients with chronic disease .
c) Reinforce energy conservation activities like taking rests periods and maintaing pace.
d) Organize all the activities and environment beforehand to conserve energy and reduce fatigue.
e) Instruct patient to avoid caffeine and other stimulating food before bed as it can contribute to fatigue and interrupt sleep pattern.
f)Encourage a warm bath or washers immediately before bedtime for relaxation.
f) Reposition the patient in certain time periods to promote comfort .
g) Administer a night time analgesic and / or a long acting anti-inflammatory drug as prescribed to alleviate pain and facilitate sleep.
4. Deficient knowledge related to treatment / complexity of treatment possibly evidenced by verbalizing inaccurate information / multiple questions / request for information.
Interventions:
a) Assess the patient's knowledge of disease , management and complication .
b) Educate the disease process information as the unknown case, chronicity of SLE, processes of inflammation, control versus cure.
c)Introduce information on drug therapy and instruct patient about potential side effects of steroids, immunosuppresant drugs.
d) Patient should be stressed on not altering or stopping steroids as they wish .
e) Instruct the patient to monitor for signs of fever as it is a common manifestation of SLE.
f) Instruct in adapting a healthy lifestyle activities that helps to reduce flare-ups such as eating a balanced diet, regular exercise, avoiding sun, adequate rest.
g) Provide information on appropriate clinical trials .
h) Always be cooperative and a good listener to patient's misunderstanding or concerns about disease.
Prepared by : RN Dawa Lhomu Sherpa (Yangla )
BSc. Nurse , Nepal


Good one
ReplyDeleteThankyou very much .
Delete